The latest updates to SimCenter research application tools are summarized below. All applications are open-source, compatible with Tapis Version 3, and feature an integrated auto-citation generator. Download the updated releases to take advantage of changes made to input and output formats. A two-page summary of each application and "how to cite" attributions are provided on each tool webpage.
 quoFEM Version 4.0 incorporates changes required to interact with DesignSafe and the Tapis Version 3 interface
quoFEM Version 4.0 incorporates changes required to interact with DesignSafe and the Tapis Version 3 interface
The quoFEM application provides uncertainty quantification methods (forward, inverse, reliability, sensitivity, parameter estimation, and surrogate modeling) to natural hazards researchers who utilize simulation software applications in their research. Version 4.0 incorporates changes required to interact with DesignSafe and the Tapis Version 3 interface.
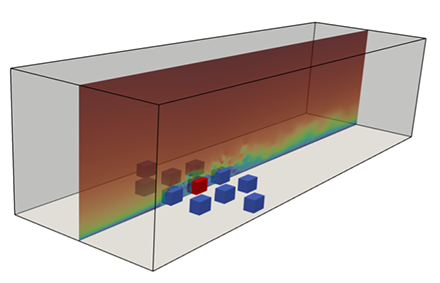 WE-UQ Example 4.9 simulates wind loads on a building with surroundings
WE-UQ Example 4.9 simulates wind loads on a building with surroundings
The WE-UQ application is open-source software that provides researchers a tool to assess the response of a building to wind loading. The application incorporates uncertainty quantification in the structure’s response to account for the user’s assumptions of the building properties and numerical modeling. Version 4.1 includes the capability for surrogate models, and it includes Example 4.9 that simulates wind loads on a building with surroundings.
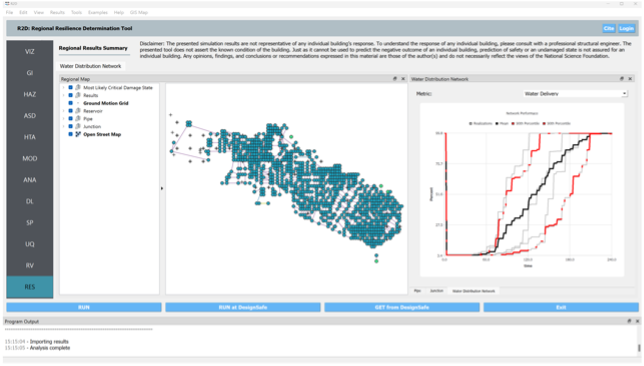 R2D Example E16 uses REWET for performance evaluation and recovery simulation of water distribution systems
R2D Example E16 uses REWET for performance evaluation and recovery simulation of water distribution systems
The Regional Resilience Determination Tool (R2D) creates and launches simulation workflows to assess the regional impact of natural hazard events. R2D advances the capabilities of the natural hazards engineering community by facilitating the high-resolution assessment of disaster impact and risk on a regional scale. Version 5.1 includes the expansion of the SimCenter Damage and Loss Model Library to include detailed water pipeline damage and loss models, and it includes Example E16 which uses REWET for performance evaluation and recovery simulation of water distribution systems.
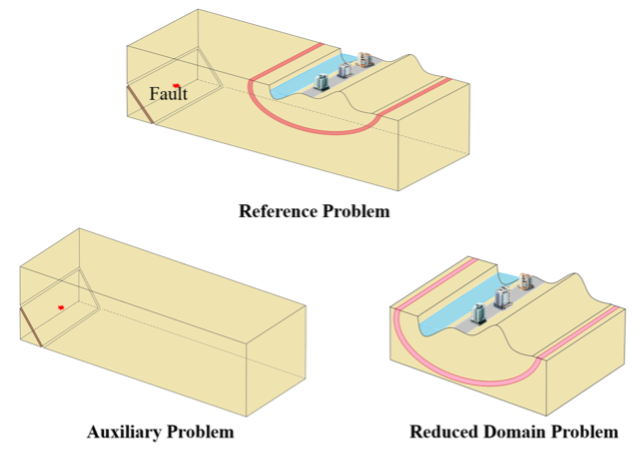 EE-UQ Version 4.1 includes a Domain Reduction method to create events for buildings given large physics-based simulations
EE-UQ Version 4.1 includes a Domain Reduction method to create events for buildings given large physics-based simulationsThe Earthquake Engineering with Uncertainty Quantification (EE-UQ) application creates and launches simulation workflows to assess the response of a structure subjected to earthquakes. Version 4.1 includes a Domain Reduction method to create events for buildings given large physics-based simulations. It also includes an OpenSees@DesignSafe option to allow users to run OpenSees, OpenSeesMP, OpenSeesSP, and OpenSeesPy simulations utilizing TACC HPC resources from their desktop.
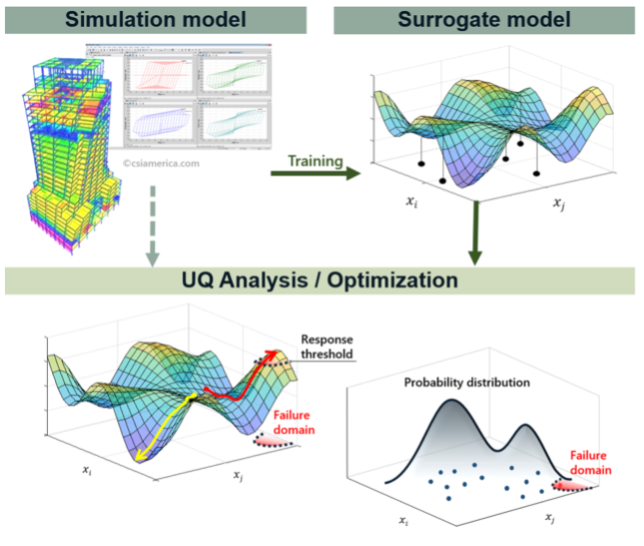 PBE Version 4.1 includes the capability for surrogate models, and it includes a Domain Reduction method to create events for buildings given large physics-based simulations
PBE Version 4.1 includes the capability for surrogate models, and it includes a Domain Reduction method to create events for buildings given large physics-based simulations
The Performance Based Engineering (PBE) application simulates the impact of a natural hazard event on a building or other structure. The impact is quantified in a probabilistic approach using the Pelicun damage and loss assessment engine. Version 4.1 includes the capability for surrogate models, and it includes a Domain Reduction method to create events for buildings given large physics-based simulations. It also includes an OpenSees@DesignSafe option to allow users to run OpenSees, OpenSeesMP, OpenSeesSP, and OpenSeesPy simulations utilizing TACC HPC resources from their desktop.